Acceleration Drawing
Acceleration Drawing - Web set the position, velocity, or acceleration and let the simulation move the man for you. View this simulation to predict, qualitatively, how an external force will affect the speed and direction of an object’s motion. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. How do we calculate acceleration in general. We define acceleration, a, as the change in velocity divided by time. Web david explains how to read an acceleration vs. Move the little man back and forth with the mouse and plot his motion. Instantaneous acceleration \(a\) is the acceleration at a specific instant in time. Figure 3.8 when acceleration is constant, the slope of 2d versus t2 gives the acceleration. The shapes of each graph relate by slope. Learn about position, velocity, and acceleration graphs. Web because acceleration is velocity in m/s divided by time in s, the si units for acceleration are m/s 2 m/s 2 size 12{m/s rsup { size 8{2} } } {}, meters per second squared or meters per second per second, which literally means by how many meters per second the velocity changes. Web to be specific, acceleration is defined to be the rate of change of the velocity. Web the acceleration vector is. Time graph must be constant. View this simulation to predict, qualitatively, how an external force will affect the speed and direction of an object’s motion. Displacement is the product of velocity and time. Finally, noting that δ v δ t = a c and that δ s δ t = v , the linear or tangential speed, we see that the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration is a c = v 2 r. Web this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs,. Again, in this pass through mechanics we will only be investigating scenarios in which the acceleration is constant. Web acceleration is the rate of change of displacement with time. The above equation says that the acceleration, a , is equal to the difference between the initial and final velocities, v f − v i , divided by the time, δ. Web acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Here, you can learn how to find acceleration in two more ways. Web the slope of the line represents the rate at which the velocity is changing, and the rate at which the velocity is changing is termed the acceleration. How do we calculate acceleration in general. Δ v δ t. Plot these values as a function of time. Web these are acceleration vs time graphs. Learn about position, velocity, and acceleration graphs. We define acceleration, a, as the change in velocity divided by time. Time graph is shown below. Finally, noting that δ v δ t = a c and that δ s δ t = v , the linear or tangential speed, we see that the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration is a c = v 2 r. Web this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs,. Web describe the motion of a particle with a constant acceleration in three dimensions. The fifth kinematic equation relates velocity, acceleration, and displacement. Web the acceleration vector is. Recall that velocity is a vector—it has both magnitude and. Plot these values as a function of time. Δ v δ t = v r × δ s δ t. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. At any point on a trajectory, the magnitude of the acceleration is given by the rate of change of velocity in both magnitude and direction at that point. Web whenever objects change their. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Web set the position, velocity, or acceleration and let the simulation move the man for you. Thus, a correct acceleration vs. It explains how to use area and slope. Web the acceleration calculator on this site considers only a situation in which an. The above equation says that the acceleration, a , is equal to the difference between the initial and final velocities, v f − v i , divided by the time, δ t , it took for the velocity to. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. This is the acceleration of an object in a circle of radius r at a speed v. Frieda toranzo jaeger, uber déjame entrar 鹿@travesiacuatro the work of frieda toranzo jaege. Acceleration can be caused by either a change in the magnitude or the direction of the velocity. Express the acceleration in unit vector notation. From the motion diagram, the acceleration of the car can be determined to be negative at every point. Web to be specific, acceleration is defined to be the rate of change of the velocity. Web a = 2 d t 2. The fifth kinematic equation relates velocity, acceleration, and displacement. Time graph must be constant. Recall that velocity is a vector—it has both magnitude and. Because object a experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Web describe the motion of a particle with a constant acceleration in three dimensions. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. Web if we divide both sides by δ t we get the following:
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors MSTC Physics

How To Draw Acceleration Graph » Hospitalrole

Acceleration Formula, Effect Of Direction On Motion Embibe
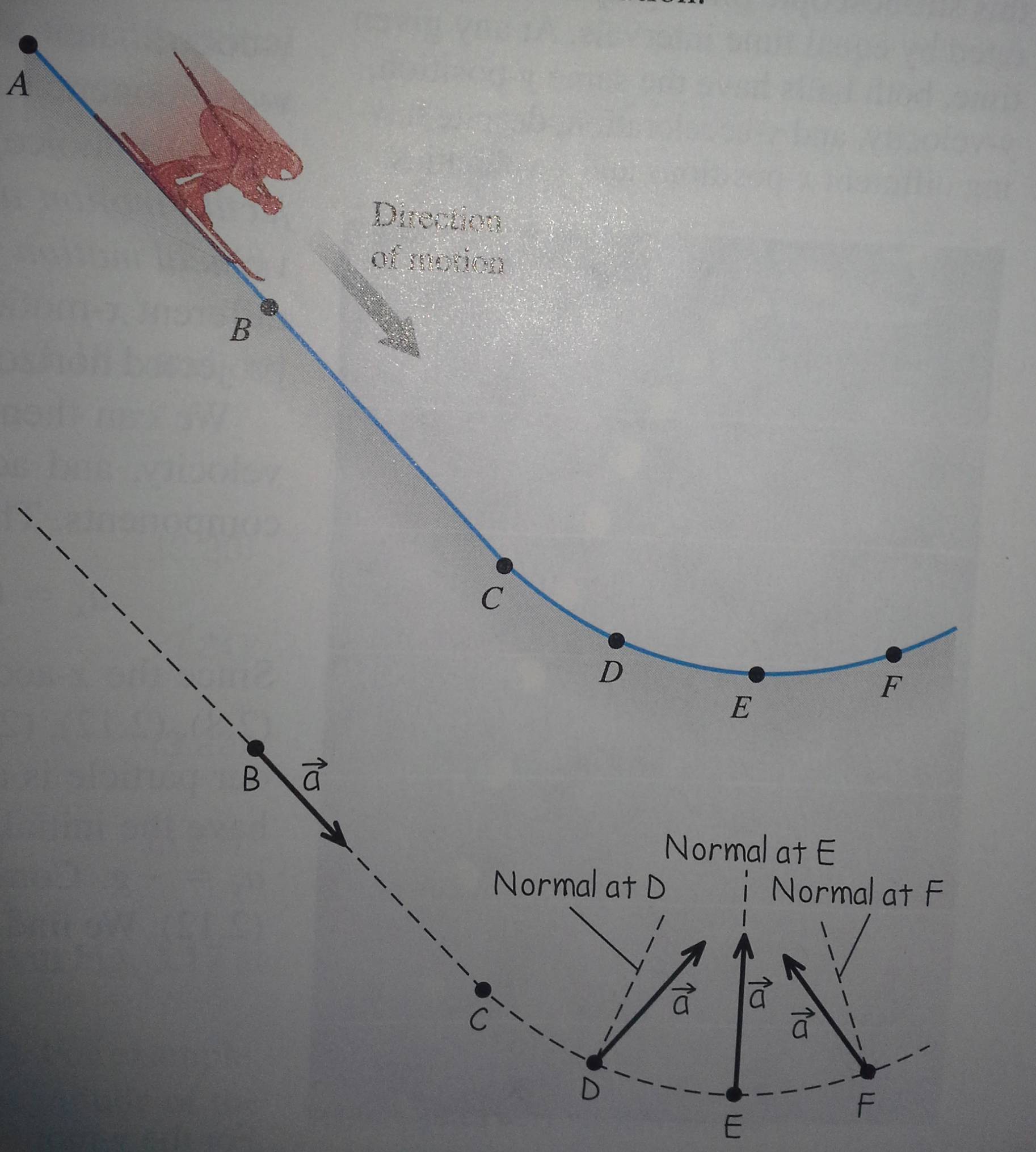
newtonian mechanics Animating an Acceleration Vector Acceleration

Diagram of Acceleration due to Gravity LuckyExam

Acceleration Vectors Example YouTube

AccelerationTime GraphGraphical Representation of Motion (Part3

Is acceleration a vector or scalar? PhysicsGoEasy

Acceleration as physics force for car movement and velocity outline

Acceleration Formula, Effect Of Direction On Motion
We Define Acceleration, A, As The Change In Velocity Divided By Time.
Δ V Δ T = V R × Δ S Δ T.
Figure 3.8 When Acceleration Is Constant, The Slope Of 2D Versus T2 Gives The Acceleration.
How Do We Calculate Acceleration In General.
Related Post: